Install the LEMP Stack on Raspberry Pi
This guide will help you set up a basic LEMP environment (Linux, Nginx, MySQL, PHP) on a Raspberry Pi running Raspbian OS. The environment will use PHP version 8.3 and MySQL version 8.0, and is intended for local use. This guide contains the minimum required steps to get the LEMP stack running on your Raspberry Pi. For troubleshooting and more advanced configurations, you can refer to the official documentation of the software components or search the internet for more detailed guides.
Complete the following steps by running the commands in the terminal on your Raspberry Pi.
1. Update and Upgrade the System
Before installing any packages, update and upgrade the system to ensure you have the latest software. This can take a minute or two, depending on your internet connection and the number of updates available. Use the following command to update and upgrade the system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
After these commands are completed, you should see an output similar to the following:
2. Install Nginx
Nginx will act as the web server for your YAFFA instance:
sudo apt install nginx -y
After the installation is complete, start the Nginx service and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
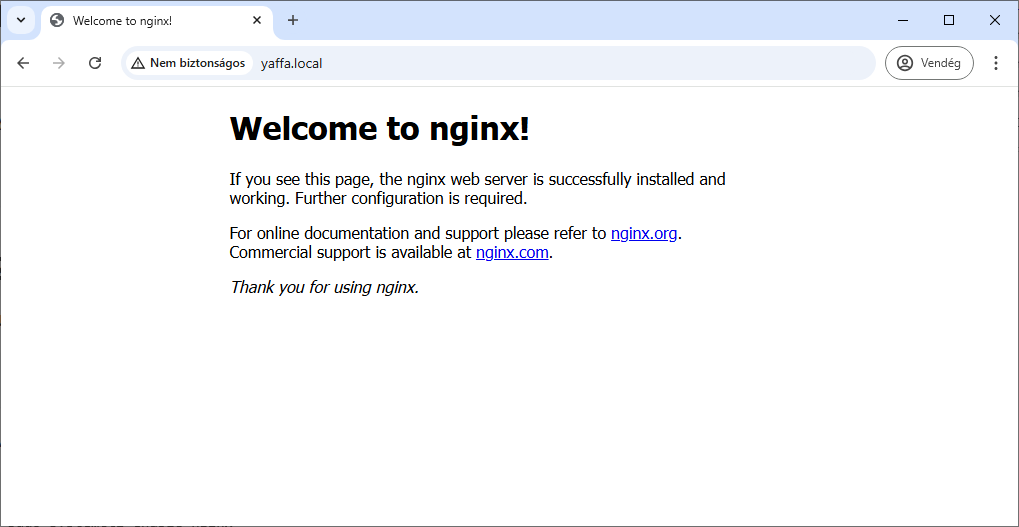
Verify that Nginx is working by visiting your Raspberry Pi's IP address in a web browser. You should see the default Nginx welcome page.
3. Install MySQL
We need to install a database server to store the data for YAFFA. MySQL is a popular choice for this purpose, but for Raspberry Pi, we need to install MariaDB, a community-developed fork of MySQL:
sudo apt install mariadb-server -y
After the installation is complete, run the MySQL secure installation script to set up the root password and other security options. Take note of the root password you set during this process.
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Log in to MySQL to ensure it's working:
sudo mysql -u root -p
You should see the MySQL prompt.
Now exit the MySQL prompt:
exit
4. Install PHP 8.3 and Required Extensions
Install PHP and necessary extensions for Laravel-based applications like YAFFA. We will install PHP version 8.3 and the required extensions.
First, we need to make some preparations by adding the PHP repository and updating the package list:
sudo wget -qO /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg
Add the PHP repository:
echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list
At this point, we need to update the package list again:
sudo apt update
Now we can install PHP 8.3 and the required extensions:
sudo apt install php8.3 php8.3-fpm php8.3-mysql php8.3-ctype php8.3-curl php8.3-dom php8.3-fileinfo php8.3-mbstring php8.3-pdo php8.3-tokenizer php8.3-xml -y
You can verify the PHP installation by checking the version:
php -v
5. Configure Nginx
Edit the Nginx configuration file to serve YAFFA:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/yaffa
Add the following configuration to the file. Adjust the server_name and root directives to match your setup, if needed. In this given example, we are using yaffa.local as the server name and /var/www/yaffa as the root directory, which can be set up using raspi-config.
server {
listen 80;
server_name yaffa.local;
root /var/www/yaffa;
index index.php index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Enable the configuration and reload Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/yaffa /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo systemctl reload nginx
6. Test your LEMP Stack
Create a directory for YAFFA and set the correct permissions:
sudo mkdir /var/www/yaffa
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/yaffa
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/yaffa
At this point it is also worth adding your user to the www-data group to avoid permission issues when working with the files in the /var/www/yaffa directory. E.g.
sudo usermod -a -G www-data pi
You need to log out and log back in for this change to take effect.
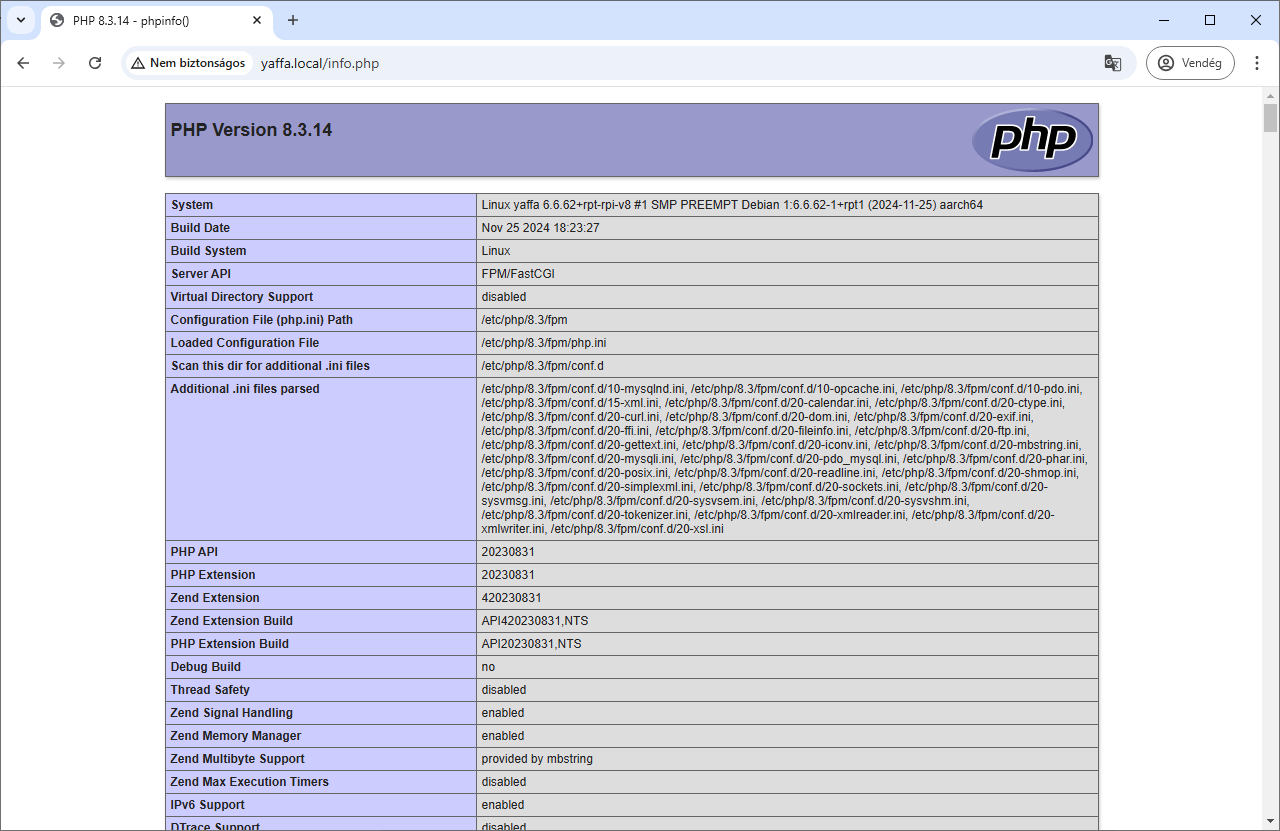
Let's test if everything is working correctly. Create a PHP info file in the web root directory:
echo "<?php phpinfo();" | sudo tee /var/www/yaffa/info.php
Visit http://<your-ip-address>/info.php in your web browser. You should see the PHP information page.
7. A few additional steps
Your device is now set up with a basic LEMP stack. Before proceeding with the installation of YAFFA, you need to take a few additional steps, to have some tools that will be needed during the installation process.
Install Composer
Composer is a dependency manager for PHP. Install it by running the following commands:
sudo apt install composer -y
Install Git
Git is a version control system that is used to download the YAFFA source code. Install it by running the following command:
sudo apt install git -y
Conclusion
Congratulations! Now you can proceed with the installation of YAFFA by following the installation guide.
As a reminder, this guide is intended to set up your environment for local use. If you plan to host YAFFA on a public server, additional security measures should be taken.